Capital Stacking Loan: How Smart Investors Structure Funding for Real Estate and Business
If you’re raising money for a large real estate acquisition or growing your business with outside capital, understanding the capital stack is non-negotiable. The way you structure your funding directly impacts risk and returns so its important to have a strategy when it comes to capital stacking loans.
I will explain what a capital stacking loan is. I will also show how it works in real estate and business lending. Finally, I will talk about how smart investors use this information. They improve cashflow, financing, reduce equity dilution, and find the best lenders for capital stacking loans.
What Is a Capital Stacking Loan?
A capital stacking loan is a structured financing strategy that layers different types of funding, each with its own risk, return, and repayment terms, to fund a single project or deal. This strategy is widely used in commercial real estate, mergers and acquisitions, and startup expansion.
In real estate, capital stacking typically includes senior debt, mezzanine debt, preferred equity, and common equity. In a capital stacking business loan, layers may include term loans, lines of credit, convertible debt, and equity investment.
The goal? To build a financing structure that aligns investor and lender interests, manages risk, and maximizes leverage while protecting your control.
How Does Capital Stacking Work?
Think of the capital stack like a layered cake. Each layer has a different level of priority and risk:
- Senior Debt (Lowest risk, lowest return): This is typically a bank loan or mortgage secured by the asset. It gets repaid first and usually has the lowest interest rate.
- Mezzanine Debt (Moderate risk/return): Subordinate to senior debt, this layer often comes from private lenders and carries higher interest rates. It may include equity kickers.
- Preferred Equity (Higher risk/return): Investors here receive fixed returns and priority over common equity holders but don’t have control.
- Common Equity (Highest risk, highest return): This includes the sponsor’s or business owner’s investment. Common equity gets paid last but also has unlimited upside.
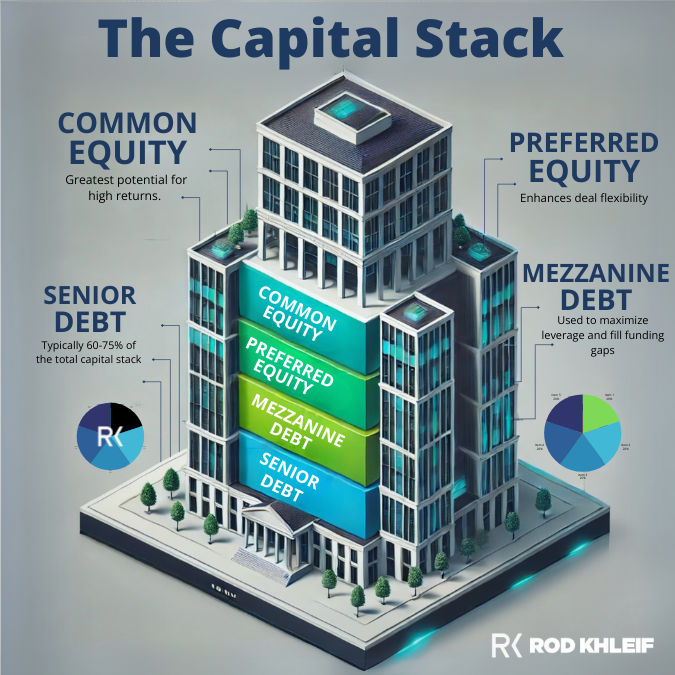
This structure allows the project owner or business operator to control more of the asset with less personal capital while still offering returns to multiple stakeholders.
Want to learn more about the cap stack? Check out our comprehensive cap stack guide.
Benefits of Capital Stacking
- Optimized Leverage: Use more financing with less out-of-pocket capital.
- Investor Alignment: Give different classes of investors different roles, returns, and timelines.
- Risk Management: Higher-risk investors take higher positions in the stack, protecting senior lenders.
- Flexible Terms: Mix and match funding sources based on your needs and timeline.
Whether you’re funding a $10 million apartment complex or a growing e-commerce brand, capital stacking can be the key to efficient, scalable growth.
Capital Stacking Business Loan: Use Cases
Capital stacking isn’t just for real estate. Many growth focused businesses use capital stacking loans to fuel expansion without over-relying on one financing type.
Common use cases include:
- Business Acquisitions: Combine SBA loans, seller financing, and equity investment.
- Startup Growth: Use venture debt, angel capital, and lines of credit.
- Franchise Rollout: Blend term loans, equipment financing, and preferred equity.
This approach is especially useful for businesses seeking to avoid heavy equity dilution or retain majority ownership while still accessing large amounts of capital.
How Do You Find Loan Lenders?
Not all lenders understand or offer layered capital solutions. When seeking capital stacking loan lenders, look for:
- Experience with Structured Finance: Lenders who work in CRE, M&A, or venture lending.
- Custom Deal Structuring: Providers that can coordinate with other lenders or equity partners.
- Speed and Flexibility: Especially for bridge loans or mezzanine funding.
You may need to work with multiple parties, including banks, private lenders, equity investors, and specialized capital advisory firms.
Capital stacking is an advanced strategy if done right, unlocks powerful investment and business growth opportunities. If you invest in real estate or run a business, knowing the capital stack can help you grow wisely. It can also protect your equity and help you work with lenders who understand layered finance.
If you’re evaluating a deal or building your stack, don’t go it alone. Work with capital advisors, commercial lenders, or business finance experts to help structure the most strategic stack possible.
FAQ: Capital Stacking Loan Strategy
Q: What exactly is a capital stacking loan?
A capital stacking loan is a structured financing method that combines multiple types of funding, like senior debt, mezzanine debt, and equity, to finance one deal. Each layer of the “stack” carries different risk, return, and repayment priority.
Q: Why is capital stacking used in real estate investing?
Capital stacking allows real estate investors to use more leverage. It helps them bring in different types of investors. This method also reduces the amount of their own cash they need. It’s how you take down large commercial deals while managing risk and return across the board.
Q: What’s the difference between senior debt and mezzanine debt?
Senior debt is your first lien mortgage. It has the lowest risk, lowest cost, and paid first. Mezzanine debt sits behind that and is riskier, so it comes with higher interest and sometimes equity participation. Both are common in capital stacking real estate deals.
Q: How is capital stacking used in business loans?
In a capital stacking business loan, you might combine an SBA loan with seller financing, private equity, or a working capital line. The idea is to customize your financing, so you don’t rely too heavily on any one source or give up too much control.
Q: Is capital stacking only for big deals?
No. While it’s common in large commercial real estate or M&A deals, smart investors and entrepreneurs use capital stacking principles for small business expansion, real estate flips, or mid-size multifamily deals. It’s about structure, not size.
Q: What’s preferred equity, and where does it fit?
Preferred equity sits between mezzanine debt and common equity. These investors receive a set return before common shareholders get paid. However, they usually do not have voting rights or control. It’s a popular middle ground in the capital stack.
Q: How do I find capital stacking loan lenders?
Look for lenders experienced in commercial real estate, M&A, or venture lending. These capital stacking loan lenders understand layered finance and can coordinate with other funding partners like private equity or family offices.
Q: Can I structure a capital stack myself?
You can, but I don’t recommend going solo on your first deal. Work with an experienced capital advisor or commercial lender who understands structured finance. It’ll save you time, stress, and potentially costly mistakes.
Q: What are the risks of capital stacking?
The more complex the stack, the more moving parts you’re managing. Misaligned incentives, repayment disputes, or changing interest rates can impact performance. That’s why clarity, contracts, and capable advisors are key.
Q: How does capital stacking impact investor returns?
It can improve returns for those higher up the stack, like common equity holders but it also concentrates risk. A well-structured stack balances upside potential with protection, depending on each investor’s role and risk tolerance.
Q: Is capital stacking legal and SEC-compliant?
Absolutely, but if you’re raising money from multiple investors, especially in real estate syndications, you must stay SEC compliant. Work with syndication attorneys to ensure your private placement memorandums and offering documents are done right.
Q: What industries use capital stacking business loans?
Industries like commercial real estate, franchising, e-commerce, private equity rollups, and tech startups commonly use capital stacking. Any business that needs growth capital but wants to manage dilution and risk can benefit.
Q: Where can I learn more about how syndicators structure capital stacks?
Download our Guide to Apartment Building Syndications or join our Multifamily Bootcamp. We walk through real-world examples of capital stacking, investor returns, and legal structuring all with hands-on coaching.
Want to learn how real estate syndicators and business owners stack capital for maximum leverage?
Join our next bootcamp!
Download our guide to apartment building syndications.
Disclaimer: This post was written with the help of AI and edited by Rod and his team.



